Technical Skills And Innovations
In today’s industry, technical skills and innovations are key drivers of competitiveness and growth. They are sold across various sectors, including tech, manufacturing, healthcare, and finance. Here’s a breakdown of the main categories of technical skills and innovations currently in demand:



These technical skills and innovations are transforming industries, but they come with challenges. Staying ahead of these trends requires continuous learning, but mastering them can open up numerous opportunities in the global job market.
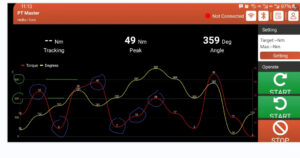
Accuracy Guaranteed: Understanding Calibration for Your High-Torque Cordless Wrench The

Why High Torque Cordless Wrenches are Replacing Hydraulic Tools The